
Privacy statement: Your privacy is very important to Us. Our company promises not to disclose your personal information to any external company with out your explicit permission.
The non-stop electronic billing system (ETC) is a fully automatic electronic toll collection system for highways, bridges and tunnels. It is used to solve the congestion of highway toll gates, save highway land resources and save energy and reduce emissions. Effective means. Compared to the manual semi-automatic charging method being used, the electronic non-stop charging technology can increase the lane capacity by 3 to 5 times. The ETc system enables wireless communication between the vehicle and the toll booth through an automatic vehicle identification system (AVI) and real-time online interaction of charging information. Through the short-distance dedicated communication between the vehicle's RFID system and the roadside tolling unit, the ETC system can complete the entire charging process without any other human collaboration. The article designed an antenna for the ETC system for its onboard (OBU) unit.
In order to meet the requirements of miniaturization, wideband, and circular polarization, many microstrip antenna forms have been studied. The circular polarization bandwidth of a conventional single-chip microstrip antenna is very narrow, generally not exceeding 1%. Using the microstrip antenna array technology, the bandwidth can be increased to a large extent, but the structure of the antenna is complicated. For a single-strip microstrip antenna, some new feed technologies can be used to effectively widen the circular polarization bandwidth of the antenna. For example, using coplanar waveguide feeding, L-type feeding, doubly-fed or four-feeding technology, etc., although the bandwidth is greatly improved, the structure is also complicated.
Based on a single patched circular microstrip antenna, an antenna model with cross-caliber coupling feed is designed. This kind of feeding mode is easy to generate circularly polarized waves, and its impedance matching and frequency bandwidth can be obtained. The ideal result is that the designed antenna model can fully meet the requirements of miniaturization, wideband and gain.
1 antenna structureIn order to achieve the characteristics of the wide frequency band, the antenna adopts a caliber-coupled feeding mode. Compared to coaxial or microstrip feeds, caliber-coupled feeds have some significant advantages: no solder joints at the feed, many tunable parameters for impedance matching, and feed-structures and bases for radiating patches The sheets are separated from each other, and different dielectric materials and dielectric thicknesses can be independently selected to meet the needs of the feed structure for the radiation patch; by adjusting the length of the coupling gap or the length of the open end of the microstrip feeder, it is easier than other feeding methods. The ground and the radiation patch achieve impedance matching and the like. The article uses the characteristics of the feed structure and the substrate of the radiation patch to separate from each other, and uses a radiation substrate with a low dielectric constant and a large thickness to reduce the Q value of the antenna, thereby achieving the purpose of widening the bandwidth. In addition, the ground plane can shield the parasitic radiation from the feeder from interference with the radiation pattern in the upper half of the antenna.
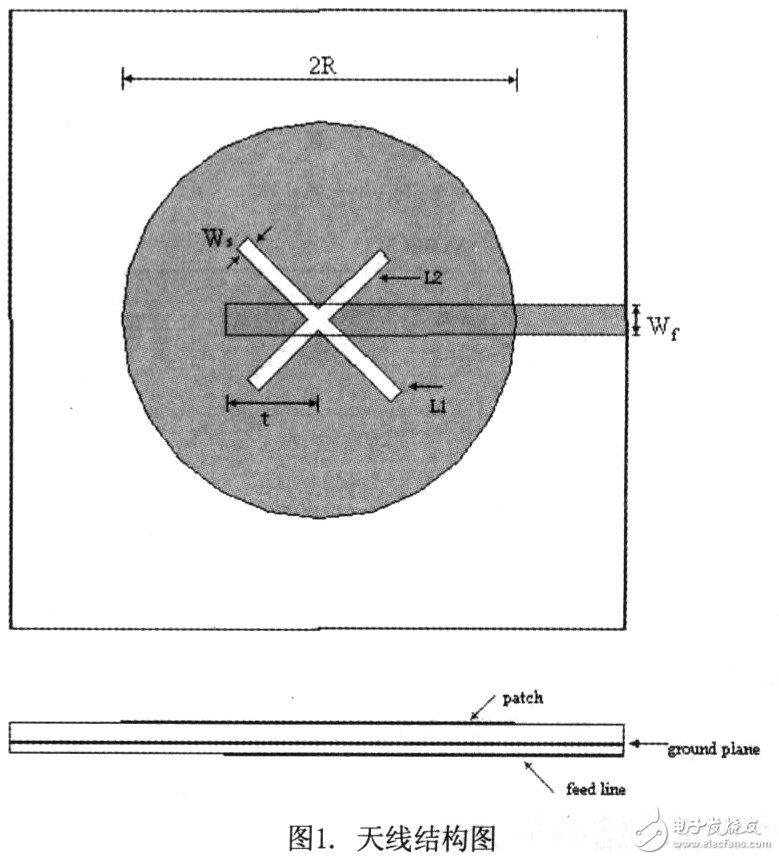
The designed antenna model is shown in Figure 1. The radiation patch adopts a circular patch with a radius of R=12.8 mm. The bottom of the patch is an air dielectric layer with a thickness of 2 mm. In practical applications, considering the firmness and impact resistance of the antenna structure, It is considered to use a material such as a foam having a similar dielectric constant for filling. Below the air dielectric layer is a ground plane that opens the cross-shaped coupling slot. The arms of the cross-coupling groove are unequal in length, L1 is 14 mm long, L2 is 12 mm long, and the length ratio is about 1.17. The gap width is WS=1mm. This value can be flexibly adjusted in practical applications, as long as the WS is much smaller than L. Below the ground plane is an FR4 feed substrate with a dielectric constant of 4.4 and a thickness of 1 mm. Below the feed substrate is a microstrip feed line with a width Wf=2 mm to ensure that the input impedance of the feed line is about 50 ohms. The two arms of the microstrip feed line and the cross-shaped coupling groove are offset by 45 degrees. The distance from the open end to the center point is 6 mm to ensure that the input impedance of the microstrip antenna is well matched.
The article uses the HFSS software of Ansoft based on the finite element method for simulation design. The S11 scattering parameter map and the axial ratio diagram of the obtained antenna are shown in Fig. 2 and Fig. 3. It can be seen from Fig. 2 that the antenna resonates at 5.8 GHz, and the lowest value of the scattering parameter of the frequency point S11 can reach 33 dB, indicating that the antenna is well matched, and the impedance bandwidth of the antenna VSWR 2 is about 6.9%. The circular polarization bandwidth with an axial ratio of less than 3 dB is about 3.8%. The far-field pattern and gain of the antenna are as shown in Fig. 4. The maximum gain in the side-shooting direction (θ = 0°) is 7.6 dB.

For line-polarized patch antennas that use a single slot for aperture coupling, the transmission line model proposed by Himdi has proven to be a good applicability. In the article, we can apply this method to Figure 1 by equating the cross gap into two separate slits that are perpendicular to each other, that is, the antenna is equivalent to two mutually orthogonal linearly polarized antennas. The analysis of the circularly polarized antenna shown.
The cross-shaped slits excite two mutually orthogonal modes in the patch, and we can analyze the two modes independently in the microstrip patch antenna. The equivalent transmission line model of the antenna is shown in Figure 2.

June 28, 2024
Mail an Lieferanten
June 28, 2024

Privacy statement: Your privacy is very important to Us. Our company promises not to disclose your personal information to any external company with out your explicit permission.

Fill in more information so that we can get in touch with you faster
Privacy statement: Your privacy is very important to Us. Our company promises not to disclose your personal information to any external company with out your explicit permission.